 Yellow fever is preventable by immunization. Travelers to countries with yellow fever should get the yellow fever vaccine.
Yellow fever is preventable by immunization. Travelers to countries with yellow fever should get the yellow fever vaccine.- Yellow fever is a tropical disease that is spread to humans by infected mosquitoes.
- Many yellow fever infections are mild, but the disease can cause severe, life-threatening illness.
- Yellow fever is found only in Africa and South America.
What is yellow fever?
Yellow fever is a tropical disease that is spread to humans by infected mosquitoes.
What is the infectious agent that causes yellow fever?
Yellow fever is caused by the yellow fever virus.
Where is yellow fever found?
Yellow fever is found only in parts of South America and Africa. There are two kinds of yellow fever, spread by two different cycles of infection.
Jungle yellow fever is mainly a disease of monkeys. It is spread from infected mosquitoes to monkeys in the tropical rain forest. People get jungle yellow fever when they put themselves in the middle of this natural cycle and are bitten by mosquitoes that have been infected by monkeys. Jungle yellow fever is rare and occurs mainly in persons who work in tropical rain forests.
Urban yellow fever is a disease of humans. It is spread by mosquitoes that have been infected by other people. Aedes aegypti is the type of mosquito that usually carries yellow fever from human to human. These mosquitoes have adapted to living among humans in cities, towns, and villages. They breed in discarded tires, flower pots, oil drums, and water storage containers close to human dwellings. Urban yellow fever is the cause of most yellow fever outbreaks and epidemics.
How do people get yellow fever?
People get yellow fever from the bite of an infected female mosquito. The mosquito injects the yellow fever virus into the bite.
What are the signs and symptoms of yellow fever?
Many yellow fever infections are mild, but the disease can cause severe, life-threatening illness. Symptoms of severe infection are high fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, vomiting, and backache. After a brief recovery period, the infection can lead to shock, bleeding, and kidney and liver failure. Liver failure causes jaundice (yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes), which gives yellow fever its name.

How soon after exposure do symptoms appear?
Symptoms start 3 to 6 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
How is yellow fever diagnosed?
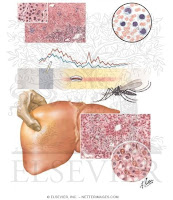
Yellow fever is diagnosed by a blood test.
Who is at risk for yellow fever?
People are at risk if they travel to an area where there is yellow fever in humans or monkeys and there are mosquitoes to spread the virus.
What complications can result from yellow fever?
Severe yellow fever infections can be fatal.
What is the treatment for yellow fever?
There is no specific treatment for yellow fever. Persons with yellow fever should rest and drink plenty of fluids. They should be kept away from mosquitoes for the protection of others. Most people get better after a long recovery period.
How common is yellow fever?
Yellow fever is common in West and Central Africa and in parts of South America. Periodic epidemics in Africa lead to hundreds of thousands of cases. Yellow fever is a very rare cause of illness in U.S. travelers.
Is yellow fever an emerging or re-emerging infectious disease?
Yes. There has been a dramatic re-emergence of yellow fever in Africa and South America since the 1980s.
How can yellow fever be prevented?
Yellow fever can be prevented by vaccination. Travelers should also take precautions against mosquito bites when in areas with yellow fever transmission.
If necessary, get vaccinated for yellow fever before travel.
- Travelers should get vaccinated for yellow fever before visiting areas where yellow fever is found. In the United States, the vaccine is given only at designated yellow fever vaccination centers.
- International regulations require proof of yellow fever vaccination for travel to and from certain countries. People who get vaccinated should be given an International Certificate of Vaccination.
Mosquitoes that spread yellow fever usually bite during the day. Travelers should take steps to reduce contact with mosquitoes when outdoors and inside.
When outside:
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and long pants. For extra protection, treat clothing with the insecticide permethrin.
- Use insect repellent on exposed skin. The most effective repellents contain 20% to 35% DEET (N,N-diethylmethyltoluamide). Follow application instructions carefully when using these products.
Stay in well-screened areas as much as possible.
- Spray living and sleeping areas with insecticide.
- Use a bednet when sleeping in a room that is not screened or air conditioned. For extra protection, treat the bednet with the insecticide permethrin.